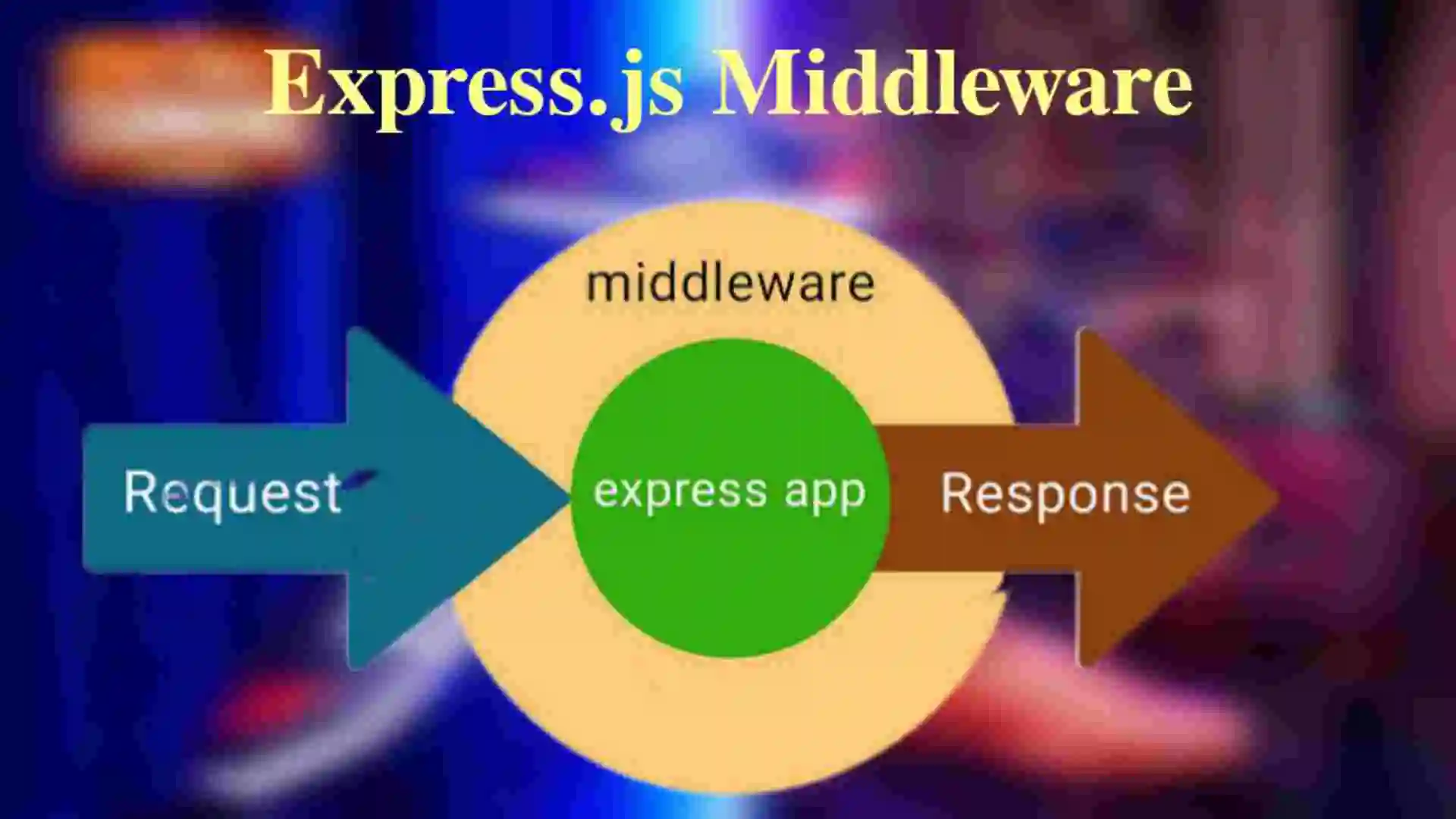
Express.js Middleware: The Backbone of Your Web Application.
The Express.js middleware functions are essential building blocks that handle requests and responses. They act as intermediaries between request and response.
In our previous posts discussion we show Express.js and its routes, let’s dive deeper into a crucial component of your express.js web applications.
What is Express.js Middleware?
Express.js Middleware is a function that has access to the request object (req), response object (res), and the next middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle. It can perform tasks like:
- Modifying the request object: Adding or removing data.
- Modifying the response object: Setting headers, cookies, or the response body.
- Ending the request-response cycle: Short-circuiting the chain and sending a response directly.
- Calling the next middleware function: Passing the request to the next middleware in the chain.
Types of Middleware
Application-Level Middleware:
- Applied to all incoming requests.
- Typically used for tasks like logging, parsing request bodies, and setting headers.
Example
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('Request received:', req.url);
next();
});Router-Level Middleware:
- Applied only to requests that match a specific route or route pattern.
- Often used for authentication, authorization, or specific route-related tasks.
Example
app.get('/protected', (req, res, next) => {
// Authentication middleware
if (!req.isAuthenticated()) {
return res.redirect('/login');
}
next();
}, (req, res) => {
// Protected route handler
res.send('Welcome to the protected area!');
});Error-Handling Middleware:
- Specifically designed to handle errors that occur within your application.
- Should be placed after all other middleware.
Example
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err);
res.status(500).send('Internal Server Error');
});Other types of Exress.js Middleware
Built-in Middleware
These built-in middleware functions are designed to handle specific tasks and are often used in most Express.js applications.
Express.js provides several built-in middleware functions that are commonly used:
express.static(): Serves static files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.express.json(): Parses JSON request bodies.express.urlencoded(): Parses URL-encoded request bodies (commonly used for form data).express.cookieParser(): Parses cookies from the request.
Custom Middleware
Custom middleware is created by you to handle specific tasks that are not covered by the built-in middleware. This allows you to tailor your application’s behavior to your exact needs.
Here are some examples of custom middleware
- Authentication middleware: Checks if a user is logged in and authorized to access a resource.
- Error handling middleware: Catches and handles errors that occur in your application.
- Logging middleware: Records information about requests and responses for debugging and analysis.
- CORS middleware: Configures CORS headers to allow requests from different domains.
- Rate limiting middleware: Limits the number of requests a client can make within a certain time period.
To create custom middleware, you need to define a function that takes three parameters: req (request object), res (response object), and next (a callback function to pass control to the next middleware or route handler). Here is a example
app.get('/protected', (req, res, next) => {
// Authentication middleware
if (!req.isAuthenticated()) {
return res.redirect('/login');
}
next();
}, (req, res) => {
// Protected route handler
res.send('Welcome to the protected area!');
});Common Uses of Middleware
- Logging: Record information about incoming requests and responses.
- Parsing Request Bodies: Extract data from POST or PUT requests.
- Authentication and Authorization: Verify user credentials and permissions.
- Static File Serving: Serve static files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Session Management: Store and retrieve user session data.
- Rate Limiting: Prevent excessive requests from a single IP address.
- Custom Response Handling: Modify or customize responses before sending them to the client.
Example
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const morgan = require('morgan'); // Third-party middleware for logging
// Application-level middleware
app.use(morgan('dev')); // Log requests to the console
//Dummy user data
const users = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Bob' },
{ id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
];
//User retrival function
const findUserById = async (id) => {
return await users.find(user => user.id == id);
}
// Route-level middleware
app.get('/users/:id', async (req, res, next) => {
const id = req.params.id;
if(id === undefined){
return next(new Error("Invalid user id."));
}
// Fetch user data (replace with your actual database logic)
const foundUser = await findUserById(id);
if(foundUser === undefined){
next(new Error("User not found"));
}
// Send the user data as a response
res.json(foundUser)
});
// Error handling middleware
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err);
res.status(500).json({Error: "Internal error"});
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server listening on http://localhost:3000');
});Conclusion
Middleware provides a flexible and modular approach to handling various aspects of your web application’s logic. You can enhance the functionality, security, and performance of your Express.js applications.
Visit Official Expreds.js website.



